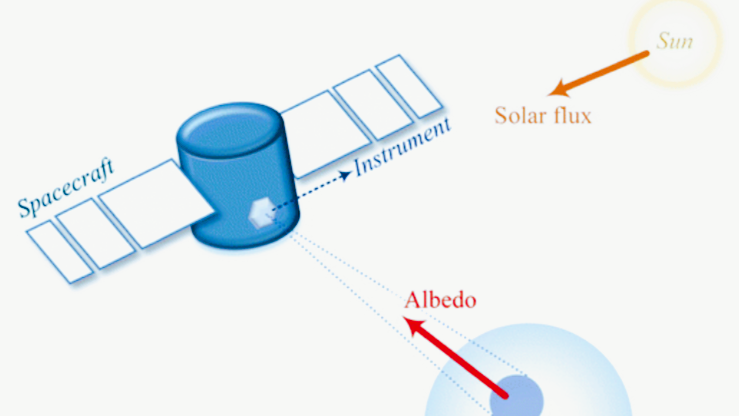
A sun sensor is a navigation instrument that specially detects the sun’s direction relative to the spacecraft. It measures the incident angle of sunlight and calculates the sun vector in the spacecraft body coordinate system. This vector serves as a core input for the attitude determination system.
Coarse Sun Sensor (CSS)
Coarse sun sensors usually consist of solar cells mounted on the spacecraft’s outer surface. They feature simple structure and low cost. They mainly support initial attitude acquisition, especially during tumbling or completely unknown attitude phases.
Fine Sun Sensor (FSS)
Fine sun sensors adopt photodiode or CCD imaging technology. They deliver much higher angle measurement accuracy. Engineers often use them for missions that require precise pointing.
Digital Sun Sensor (DSS)
Digital sun sensors integrate digital signal processing. They offer stronger anti-interference capability and better environmental adaptability. Modern small satellites and deep-space probes widely adopt them.
Working Principle of Sun Sensors
Sun sensors rely mainly on the photoelectric effect. When sunlight strikes the detectors (usually photodiodes or solar cells), it generates electrical signals. Multiple detectors arranged in specific geometry produce signal differences. Engineers use these differences to calculate the sunlight’s incident angle.
In common designs, a slit or mask sits in front of the detectors. Depending on the sun’s position, it creates different shadow or spot patterns. The system compares output signals from multiple detectors and obtains pitch and yaw angle information.
During attitude determination, the sun sensor outputs the “sun vector” in the spacecraft body frame. The system then compares this vector with the known inertial reference (for example, the sun position computed from ground-based ephemeris). This comparison allows estimation of the spacecraft’s attitude.
Attitude determination finds the spacecraft’s spatial orientation relative to a reference frame (usually the inertial frame or Sun–Earth line frame). Without accurate attitude information, the spacecraft cannot perform key tasks. These tasks include Earth-pointing antennas, sun-tracking solar arrays, and scientific payload targeting.
Sun sensors provide clear advantages. The sun is a very bright, highly predictable natural reference source. It remains visible in almost all orbits (except inside Earth’s shadow).
Send us a message,we will answer your email shortly!