Digital sun sensor are advanced attitude sensors. They primarily measure the sun’s azimuth angle relative to the spacecraft body. These sensors use image capture and digital signal processing technology. Therefore, they directly output discrete digital angle information. This digital design greatly improves measurement accuracy, noise immunity, and integration with modern onboard computers.
Basic Working Principle
Sunlight passes through an optical window and projects onto a photodetector array. It forms a specific light spot pattern. The internal processor then calculates the sun’s angular position in real time. It applies algorithms such as centroid computation, edge detection, or pattern recognition. As a result, the sensor provides accurate angle data along two or three axes.
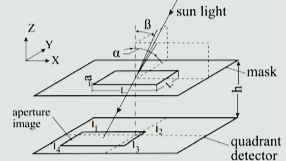
Main Types of Digital Sun Sensors
According to detector structure, optical design, and signal processing methods, engineers classify digital sun sensors into several mainstream types:
Linear Array Digital Sun Sensor
Advantages: It offers low cost, high update rates (up to tens of Hz), and easy radiation hardening.
Disadvantages: The field of view remains relatively narrow. It also shows high sensitivity to installation misalignment errors.
Area Array Digital Sun Sensor
Advantages:
– It delivers high measurement accuracy and a wide field of view (typically ±64° to ±80°).
– Advanced algorithms effectively filter out earth albedo and stray light interference.
– It suits missions that demand extremely high pointing precision, such as high-resolution earth observation satellites.
Disadvantages: It consumes more power (due to image processing). Manufacturing cost and complexity also increase.
Profile-Detecting Digital Sun Sensor
Advantages: It achieves extreme miniaturization, efficient data output, and supports wireless transmission.
Disadvantages: The technology remains in development. Commercial products are still scarce, and calibration complexity stays high.
Three-Axis Digital Sun Sensor
Advantages: A single unit provides full attitude reference. It therefore achieves very high system integration.
Disadvantages: Computation complexity increases significantly. Cost rises accordingly, so current applications remain limited.
Main Application Scenarios for Digital Sun Sensors
– Satellite attitude and orbit control — They support routine three-axis stabilization for GEO and LEO satellites.
– CubeSats and micro/nano-satellites — They provide low-cost, highly reliable attitude determination solutions.
– Deep space exploration — Models resist strong radiation and wide temperature ranges for Mars rovers or lunar landers.
– Solar sails and high-precision pointing missions — They supply accurate sun direction references.
– Ground-derived applications — Examples include solar tracking systems and UAV sun positioning.
Send us a message,we will answer your email shortly!